Throughout the world, Parkinson’s disease is on the rise due, in particular, to an aging population. Age is one of the main risk factors for this disease, which primarily affects control of motor functions.
10 M
The number of people living with Parkinson’s disease1 worldwide
60 years old
Average age when diagnosed2.
Over 12 M
The estimated number of people suffering from Parkinson’s disease worldwide by 20403.
Changes in neurons found to be linked to the disease
Parkinson’s disease results in a gradual, progressive degeneration of neurons. In particular, it involves dopaminergic neurons, which are located in the specific area of the brain responsible for producing dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in controlling movement. In the affected neurons, Lewy bodies have been found, which are composed predominantly of aggregates of the protein called alpha-synuclein.
Parkinson’s is diagnosed when more than 50% of dopaminergic neurons have been destroyed. The loss in dopamine leads to the appearance of three motor symptoms: slowness of movements, rigidity – or stiff muscles – and tremors.
The disease is complex, because other neurotransmitters may be affected by this neural degeneration. This may explain the symptoms that can arise over the course of the disease: mood changes, sleep disturbances, cognitive deficiencies, constipation, difficulty swallowing, loss of smell, urinary incontinence, etc.
In advanced stages, Parkinson’s disease leads to a gradual and full loss of independence in patients.
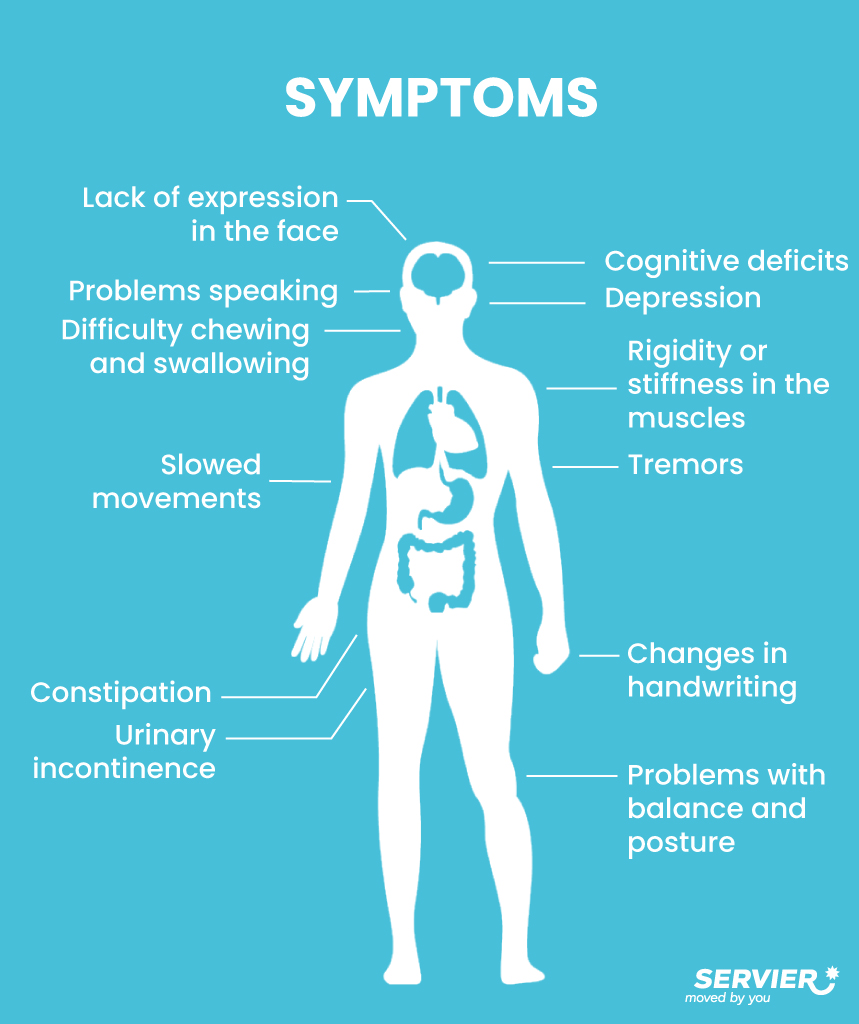
Illustrated infographic presenting the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease
A poorly understood disease whose causes are still unclear
No clearly defined cause has been identified for Parkinson’s disease, but several factors appear to contribute to its onset.
First and foremost, age; on average the disease begins between the ages of 55 and 65. Several susceptibility genes have been identified, particularly in cases of early onset of the disease before age 50. Certain environmental factors may also be responsible for the disease, in particular, exposure to neurotoxic products such as organochlorine pesticides (organic compounds containing chlorine), or heavy metals like lead, mercury, cadmium, and manganese.
Research is advancing our understanding of the causes of Parkinson’s and the mechanisms responsible for neuronal degeneration and the onset of symptoms. Today, researchers are taking an interest in the mechanisms that could slow neuronal degeneration, or even put a stop to it — with the goal being to preserve patient autonomy and improve their quality of life.
Research is currently exploring the involvement of alpha-synuclein over the course of the disease . This protein, which plays a role in signal transmission between neurons, is abnormally abundant in the neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease. The reason for this accumulation is still unclear at this time.
What therapeutic solutions are available?
Several treatments exist to overcome dopamine deficiency, which help manage motor symptoms but do not slow disease progression.
The main treatment available is a precursor of dopamine, called L-Dopa, which helps restore motor function for a few years, results in a significant improvement during the first months/years after treatment begins, but the effect subsequently diminishes. What’s more, this treatment causes side effects, such as involuntary movements.
Increase neuronal activity
Other types of drugs increase the activity of dopaminergic neurons, either by binding to dopamine receptors or by inhibiting the degradation of existing dopamine. These pharmacological treatments carry the risk of side effects such as confusion, drowsiness, obsessive behaviors (gambling, shopping addictions, etc.), and digestive disorders.
Deep brain stimulation
Surgery may be recommended when the disease is advanced and the patient no longer responds to pharmacological treatment. In this case, electrodes are implanted into specific areas of the brain to electrically stimulate neurons. The procedure is known as deep brain stimulation. It may have beneficial effects, but does not prevent the disease from progressing.
Physical activity
More generally, physical activity along with regular stretching and balance exercises can contribute to maintaining mobility and good postural balance.

ABOUT SERVIER ?
Historically committed to neuroscience, we’re focusing our focusing its research efforts on the discovery of targeted therapies that slow the progression of Parkinson’s disease, as well as some other selected movement disorders.
In June 2021, Servier and French biotech Oncodesign Precision Medicine announced the selection of a preclinical drug candidate that acts upon a protein affected in Parkinson’s. In September 2022, Servier acquired an exclusive worldwide license option to this drug candidate. The Phase I program, is ongoing.
We are developing this drug candidate for and with patients to ensure it can better meet their needs. This is why we have been partnering for several years with the patient organization, Parkinson Europe,, with whom we are regularly in contact stepsover the course of drug development phases to get patients’ and feedback.
In January 2024, we announced a new collaboration with Aitia focused on Parkinson’s disease. Aitia‘s Gemini Digital Twins will help identify subpopulations of patients who could respond favorably to Servier’s LRRK2 treatment in development. Read More
REMEMBER
1 N. Maserejian, L. Vinikoor-Imler, A. Dilley (Cambridge, MA, USA), Estimation of the 2020 Global Population of Parkinson’s Disease (PD) Meeting: MDS Virtual Congress 2020
2 www.hopkinsmedicine.org
3 vWhat next in Parkinson’s disease? Lancet. 2024 Jan 20;403(10423):219. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00094-1.

